Blog
How far is 3D printing from making cars?

With the help of the media, 3D printing appeared in the public as the image of high-tech industry, and its media influence reached its peak after 2013.
In fact, 3D printing is still essentially a manufacturing technology.Recent years have seen rapid growth, but the industry is still less than a fraction of the size of the entire manufacturing sector.
Automobile manufacturing, in the manufacturing industry may be said to be the largest, the highest comprehensive requirements.If 3D printing is one day widely used in automobiles, then we can say that 3D printing has really taken hold.So how far is 3D printing from making cars?
Check out 3D-printed automotive applications
1. Rapid prototype
The earliest time of 3D printing, is called Rapid Prototyping technology.Here’s why: At the time, its only purpose was to do rapid prototyping, which was design validation, assembly validation, functional validation, and so on.
In recent years, the most natural way 3D printing has entered the automotive industry is through rapid prototyping.For car companies, 3D printing for quick prototypes is not necessarily cheaper, but it will certainly save time.When it comes to vehicle development, time is money.
3D-printed instrument panel housing
3D printing + post-processing of electronic and electrical system housing
Metal 3D printing: Can be used for functional verification
Generally speaking, 3D printing enters the automobile industry with the role of rapid prototype, which is relatively deep.However, these applications are generally alternative rather than innovative.The ambitions of 3D printing do not stop there.
2. personalized customization
3D printing can be customized to provide each consumer with a unique car.However, this will also add additional costs, consumers are willing to pay for this cost?A success story from BMW’s Mini Cooper offers an answer.
First of all, through the ordering system of BMW Mini Cooper, you can design your favorite text and pattern.
After placing an order, you will receive the finished parts.You don’t need a professional technician to install it yourself.
I have to say, this kind of “official modification” service is quite impressive to have your favorite name and picture engraved on your car.It’s also inexpensive, at 149 euros (four parts in total, two of which are 3D printing).
The BMW Mini Cooper uses 3D printing to create new value and more enlightening than rapid prototyping.
3. Modification and repair of old cars/accident cars
The logic goes like this: if a discontinued old car breaks down, it’s a hassle to fix, and you need 3D printing.
Accident auction car, some parts are also difficult to find, may need 3D printing for use.The difference is that the repair of accident auction car is more sensitive to cost — if the repair cost is higher than the salvage value of the car, why should I repair?
4. Direct printing of cars?
Local Motors, an American company, claims to print cars directly in 3D.It’s a grand slogan, but it hasn’t had any real impact on the auto industry:
After all, it’s just printing a shell.
The alleged use of carbon fiber 3D printing, which is actually a fibre-enhanced plastic printing, is questionable as to its performance and whether it will ever pass automotive regulations.
Local Motor 3D-printed cars
China’s XEV also wants to 3D-print cars, which obviously has a clearer business model than Local Motors, and can better play to the advantages of 3D printing in design.Of course, it’s still not an easy thing to put into practice.
XEV’s 3D-printed car
Break through the key points of the core application of the car
If you’re an automotive engineer and you’ve seen 3D printing applications in all four of these areas, I guess you’re probably impatient.In fact, I am also an automotive engineer, I am impatient: whether it is rapid prototyping, personalized customization, repair modification, shell printing, this is just a corner, icing on the cake, dispensable applications.
If we want to break through the two core applications of cars, there are two key words: mass production and lightweight.
The first point is easy to understand. How can 3D printing break through the automotive industry if there are thousands of parts in a car that are not 3D printed?
Conversely, if any part that is not too small is made using 3D printing, the output value of that part may exceed that of the entire 3D printing industry today.
However, how difficult is it to find this point of mass production application?
3D printing is expensive, and the car industry is extremely cost-sensitive.Why was 3D printing pioneered in aircraft manufacturing?In a car manufacturing is not very cost sensitive.
3D printing is slow, and the auto industry has high production requirements.China makes 30m cars a year, while Airbus makes fewer than 1,000 aircraft a year.
Unless, that is, 3D printing creates unique value.
One person examines every part of a car and concludes that 3D printing is no match for traditional manufacturing.
This conclusion is correct, but there is a misconception.That is, design and technology are inseparable, all the parts of the car are based on the traditional manufacturing process design, 3D printing can be compared to that is strange!
If you want to find the advantages of 3D printing parts, you must combine the design and process!
According to Aaron Saunders, a vice president in Boston, the secret to being lightweight lies in 3D printing.The density of 3D-printed steel and aluminum will not be lower than that of stamping and casting. In order to achieve lightweight, design efforts must be made.
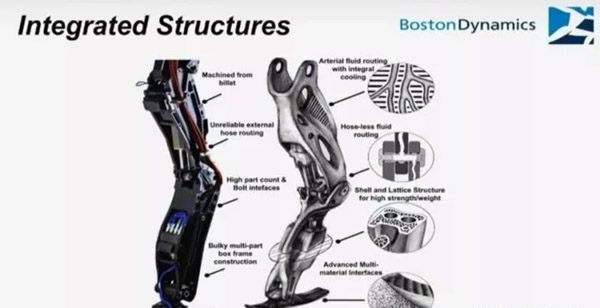
Let’s take a look at how 3D printing has led to the evolution of robotic legs:
Topology optimization and lattice structure: The “skeleton” of the right leg has an obvious hollow part, which is achieved by topology optimization to achieve lightweight;The “skeleton” part uses a lattice structure, which can be further lightened.These jobs, either by casting or by machining, are difficult to achieve.
Internal flow passage: The hydraulic pipe in the left leg is exposed to the outside, while in the right leg, it is integrated directly into the “skeleton”, which is not only more reliable, but also saves the weight and volume of fixed hydraulic pipe.
From the evolution of the legs of the Boston machine, we can see that the process change must be combined with the design change to create value.
Back in the auto industry, the lightening of fuel-powered cars can reduce fuel consumption and pollution, while the lightening of electric cars is more important — it can alleviate the problem of endurance.
Despite the potential demand, applying 3D printing to the automotive industry has been difficult.In addition to the 3D printing technology itself needs to be further improved in cost and speed, the evolution of design talents and design software is also urgent.
Design software: Traditional CAD software is mostly designed for traditional manufacturing methods. Functions such as topological optimization and lattice structure are difficult to use or useless at all.
Design talent: For decades, both industrial design and structural design have been based on the design concept of traditional technology.In the traditional concept, the topological structure and lattice structure of 3D printing are no more than “retrograde” — what is the meaning of designing a structure that cannot be processed at all?
So, it’s not just a business of 3D printing, it’s a business that needs to cross boundaries in multiple fields to move faster.